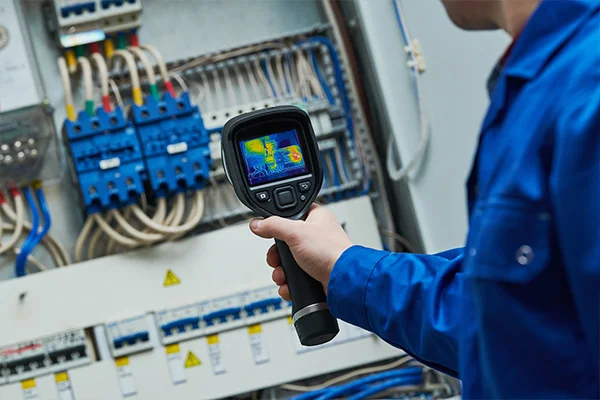
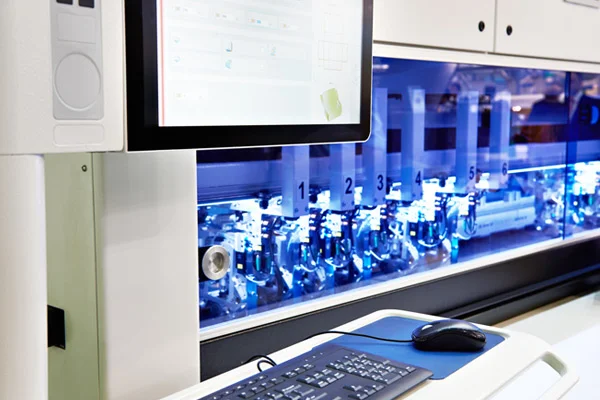
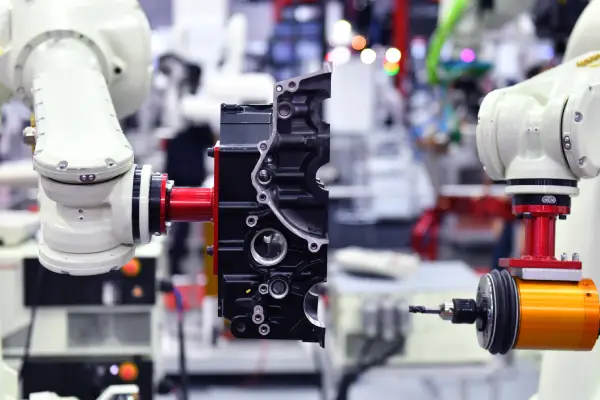
Vision Based Inspection
The Power of Vision-Based Solutions in Manufacturing by Prescient Technologies
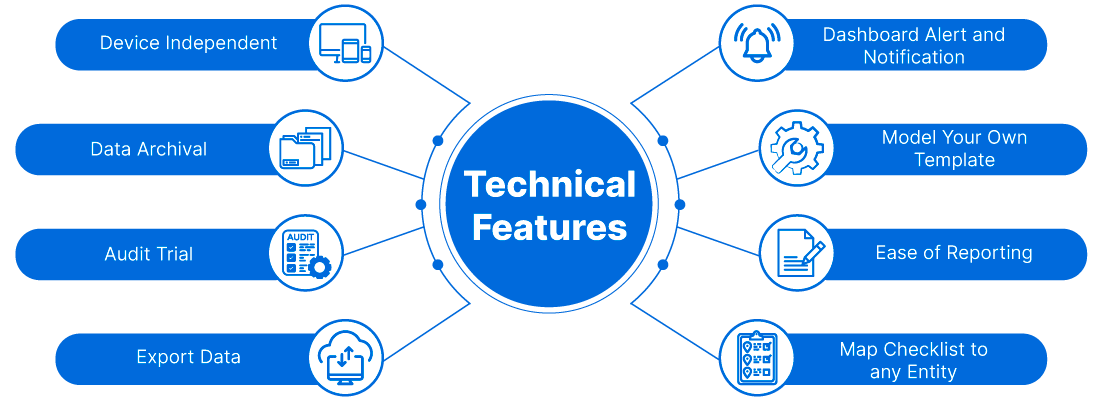
Features Of The EMIS
Features Of The EMIS

Web-based Platform
Our Digital Logbook is accessible anytime, anywhere. Whether you prefer on- premises or cloud deployment, our platform provides the flexibility to suitHighlighting how Digital Thread saves time and resources by eliminating manual data entry and transfer, allowing employees to focus on more value-added tasks your specific needs.
Customizable Checklists
Tailor your checklists to fit your unique requirements. With our platform, you can easily create and configure checklists, define the order of checklist items, and provide additional instructions for each step.
Benefits of EMIS
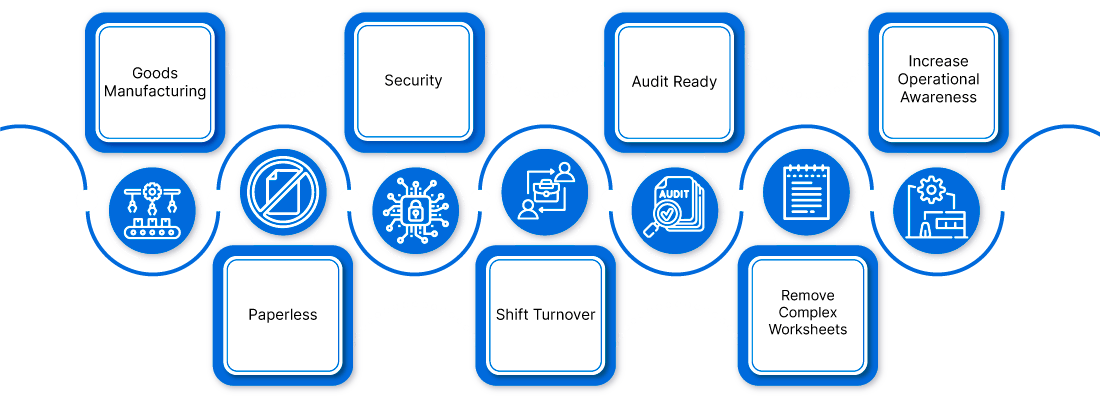
Digital Logbook Operation Rules
Functional Administrator
- Defines production lines and workshops
- Defines systems users and roles
- Configures different masters and checklists
Operator
- Views schedule
- Files checklist
- Views filled checklist
Line Incharge
- Approves filled check by operator
- Files checklist for production lines
- Monitors summary and reports
- Defines checklist-schedule for workstations
Process Incharge
- Configures different masters and checklist.
- Defines checklist-schedules.
- Files checklist for plant if applicable.
- Monitors reports and expectations from filled checklist.
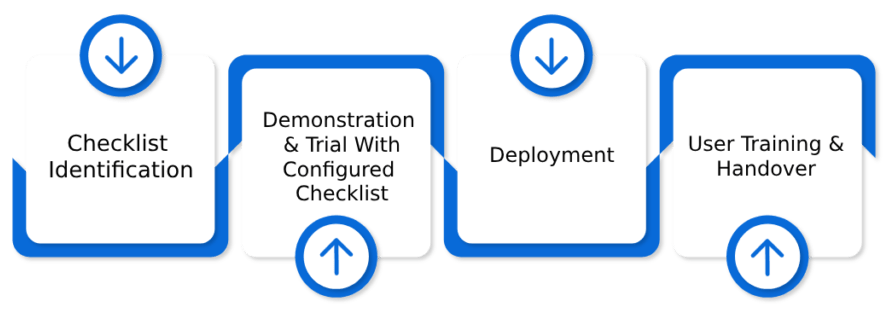
Digital Logbook Implementation
EMIS Implementation
Our Services
Our Services
Part Segregation
Utilise our Intelligent Sensing Technology Platform for precise part segregation. Employ advanced sensors such as CCTV, Laser Scanners, GPS, BLE, and UWB. Achieve streamlined operations, reduced waste, and enhanced quality control.

Defect Detection
Leverage our Intelligent Sensing Technology Platform for reliable defect detection. Utilise advanced sensors and real-time data analysis for accurate results. Prevent costly product recalls, reduce rework, and improve customer satisfaction.
End of Line Inspection
Ensure the highest quality standards with our comprehensive end of line inspection. Integrate our Intelligent Sensing Technology Platform for meticulous examination. Verify critical parameters, identify anomalies, and ensure regulatory compliance.

Dimension Inspection
Optimise 3D printing processes with our in-situ inspection services. Monitor and control the printing process in real-time using advanced sensors. Detect errors early, minimize material waste, and accelerate time-to-market.

Request a Quote Today
Schedule Free Consultation Today
Our Intelligent Sensing Technology Platform
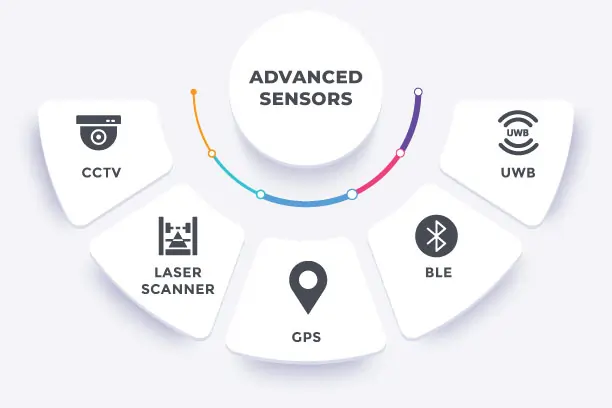
Developed by Prescient Technologies to unleash the full potential of vision based inspection
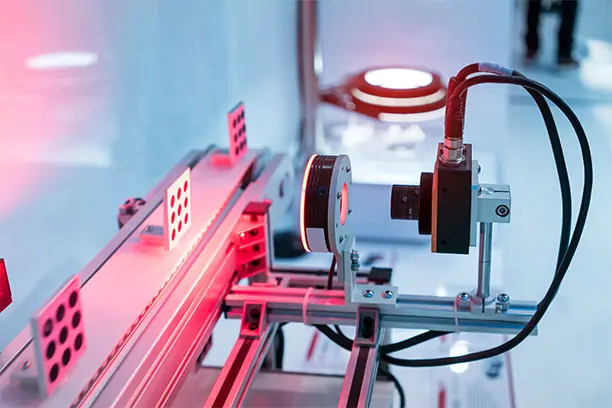

Integrates advanced sensors like CCTV, Laser Scanners, GPS, BLE, and UWB

Enables real-time data collection, high accuracy, and scalable solutions
Vision Based Inspection in Different Industries
Manufacturing
Finds surface defects, assembly errors, and misaligned parts.
Electronics
Inspects circuit boards, solder joints, and semiconductor wafers.
Automotive
Detects paint flaws, scratches, and structural issues.
Pharmaceuticals
Checks packaging, labels, and tablet quality.
Why Choose
Prescient Technologies?
-
Expertise in Engineering Process Automation
-
Successful Implementations
-
Seamless Integration and Support
-
Measurable Results

Why Choose Prescient Technologies?

Expertise and Experience
With years of industry expertise, we have a deep understanding of energy management challenges and solutions.
Cutting-Edge Technology
Our EMIS leverages the latest advancements in data analytics, machine learning, and IoT technologies to deliver optimal results.
Customized Solutions
We tailor our EMIS to fit your organization's unique requirements, ensuring a solution that aligns perfectly with your goals.
Dedicated Support
Our team is committed to your success. From implementation to ongoing support, we provide personalized assistance every step of the way.
Why Choose
Prescient Technologies

Expertise In Engineering Process Automation
Ladies she basket season age her uneasy saw. Discourse unwilling am no described dejection incommode no listening of. Before nature his parish boy.
Cyber Securitya Successful Implementations
Ladies she basket season age her uneasy saw. Discourse unwilling am no described dejection incommode no listening of. Before nature his parish boy.
Seamless Integration And Support
Ladies she basket season age her uneasy saw. Discourse unwilling am no described dejection incommode no listening of. Before nature his parish boy.
Measurable Results
Ladies she basket season age her uneasy saw. Discourse unwilling am no described dejection incommode no listening of. Before nature his parish boy.
Why Choose Prescient Technologies?
Expertise and cutting-edge technology for superior inspection services.
Elevate your quality control processes, boost productivity, and ensure customer satisfaction.
Our EMIS leverages the latest advancements in data analytics, machine learning, and IoT technologies to deliver optimal results.
Proven track record of successful projects and satisfied clients.
We tailor our EMIS to fit your organization’s unique requirements, ensuring a solution that aligns perfectly with your goals.
Vision-based inspection solutions that enhance efficiency and ensure superior product quality while reducing costs.
We tailor our EMIS to fit your organization’s unique requirements, ensuring a solution that aligns perfectly with your goals.
Dedicated Support
Our team is committed to your success. From implementation to ongoing support, we provide personalized assistance every step of the way.
What is vision based inspection ?
vision based inspection refers to the process of conducting thorough assessments and examinations in industrial settings to ensure quality control, detect defects, and maintain compliance with industry standards.
Why is vision based inspection important?
vision based inspection is crucial for identifying and addressing potential issues early in the production cycle, ensuring the delivery of high-quality products, minimizing rework, reducing waste, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
What types of services does Prescient Technologies offer for Industry Inspection?
Prescient Technologies provides a range of services, including part segregation, defect detection, end of line inspection, and in-situ inspection for 3D printing processes, all powered by our Intelligent Sensing Technology Platform.
What is the Intelligent Sensing Technology Platform?
The Intelligent Sensing Technology Platform developed by Prescient Technologies integrates advanced sensors such as CCTV, Laser Scanners, GPS, BLE, and UWB to collect real-time data and enable precise inspection in industrial settings.
How does part segregation benefit industrial processes?
Part segregation ensures the proper separation and categorization of components, minimizing errors and improving efficiency in manufacturing, assembly, and quality control processes.
How does defect detection contribute to quality control?
Defect detection allows for the identification and elimination of product imperfections, ensuring that only high-quality items are delivered to customers, reducing the risk of recalls and enhancing brand reputation.
What are the advantages of end of line inspection?
End of line inspection provides a final quality check before products are released to the market, minimizing the risk of delivering faulty items, maintaining compliance with regulations, and safeguarding customer satisfaction.
How does in-situ inspection benefit 3D printing processes?
In-situ inspection for 3D printing enables real-time monitoring and control, ensuring the quality and integrity of printed objects, reducing material waste, and accelerating the time-to-market for innovative products.
Which industries can benefit from Prescient Technologies' Industry Inspection services?
Prescient Technologies serves a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, manufacturing, and more, tailoring inspection solutions to meet the specific needs of each sector.
How can I get started with Prescient Technologies for Industry Inspection services?
To get started, simply reach out to our team by contacting us via phone or email. We'll be happy to discuss your specific requirements, provide personalized solutions, and guide you through the process.
POPULAR NEWS
Featured Posts
- March 3 2026
- systemadmin
What is the difference between EMS (Energy monitoring system) and EMS (energy management system)
Have you ever looked at your factory’s electricity bill and wondered where the energy actually goes? You see rising costs, but you do not see clear answers. Manufacturing companies across North America, Europe, and India are under pressure to reduce energy expenses and meet sustainability goals. Factory owners and engineers need visibility. R&D teams need control. Yet many organisations confuse an Energy Monitoring System with an Energy Management System. Understanding the difference between energy monitoring and energy management is essential if you want real cost savings and operational improvement. Why Energy Control Matters in Modern Manufacturing Energy costs form a large part of operational expenses in manufacturing. Smart factories now rely on connected machines, automation systems, and digital tools. As operations become more data-driven, energy performance also becomes measurable. You cannot reduce what you cannot see. But visibility alone is not enough. This is where confusion often begins. You install an Energy Monitoring System, but expect it to automatically optimise consumption. When it does not, you assume the technology failed. In reality, you may have chosen the wrong system for your goals. What is an Energy Monitoring System? An Energy Monitoring System focuses on tracking and visualising energy usage. It collects data from meters, sensors, and connected equipment. It then displays that data in dashboards or reports. A real-time energy monitoring system provides continuous visibility into consumption behaviour across machines and departments. Key Capabilities You gain transparency into where energy is being consumed. In manufacturing, this helps you – However, an Energy Monitoring System mainly observes and reports. It does not automatically control or optimise energy usage. Think of it as your energy dashboard. It tells you what is happening right now. What is an Energy Management System? An Energy Management System goes beyond monitoring. It not only collects energy data but also analyses it and drives optimisation actions. It connects energy performance with production decisions and operational planning. Core Functions Instead of just showing energy data, the system helps you reduce consumption. In manufacturing environments, an Energy Management System can – This is where the real difference between energy monitoring and energy management becomes clear. Direct Comparison: Energy Monitoring vs Energy Management To clearly understand energy monitoring vs energy management in manufacturing, the comparison below highlights operational differences. Parameter Energy Monitoring System Energy Management System Main Objective Visibility and tracking Optimisation and control Data Usage Displays energy data Analyses and acts on data Automation Level Minimal High Cost Reduction Indirect Direct and measurable Manufacturing Impact Identifies inefficiencies Corrects inefficiencies Integration Standalone dashboards Integrated with MES and production Monitoring answers:“What is my energy consumption right now?” Management answers –“How do I reduce it without affecting production?” That is the fundamental difference between energy monitoring and energy management. Why Monitoring Alone is Not Enough Many factories begin with an Energy Monitoring System. This is a logical first step because you need baseline data before improvement. But data without a strategy does not lead to savings. If you only monitor energy: An Energy Management System closes this gap. It transforms insights into structured improvement plans and measurable cost reductions. Real-World Example in Manufacturing Imagine your plant operates heavy machinery during peak tariff hours. A real-time energy monitoring system will show high consumption during those hours. It will highlight the spike clearly in your dashboard. But an Energy Management System can – This practical scenario demonstrates the operational difference between energy monitoring and energy management in manufacturing. How EMS Fits into Smart Manufacturing Industry 4.0 encourages connected systems, automation, and data-driven decision-making. Energy performance is now part of the digital factory conversation. Modern smart factories integrate: An Energy Monitoring System provides the data foundation. An Energy Management System becomes part of broader smart manufacturing software solutions, aligning energy efficiency with production efficiency. This alignment is critical for factories in the USA, Germany, France, the UK, and India, where energy costs and sustainability targets continue to rise. When Should You Choose Each System? Business Requirement Recommended System No visibility into plant energy usage Energy Monitoring System Need baseline performance data Energy Monitoring System Want measurable energy savings Energy Management System Need peak demand optimisation Energy Management System Plan to integrate with production systems Energy Management System In many cases, manufacturers start with monitoring and then scale toward management as part of digital transformation. Common Misconceptions Misconception 1: Both systems are the same. The terminology is similar, but their operational roles differ significantly. Misconception 2: Monitoring automatically reduces costs. Monitoring highlights problems. Management solves them. Misconception 3: Energy systems operate separately from production. In modern manufacturing, energy performance directly affects operational efficiency. How Prescient Technologies Supports Smart Energy Prescient Technologies has strong expertise in engineering software and digital factory systems. Its PowerConnect platform supports intelligent energy tracking and optimisation within manufacturing environments. By integrating energy systems with machine data and production workflows, you gain a structured path from simple monitoring to active management. This structured integration strengthens cost control, compliance readiness, and operational efficiency across competitive markets. Key Takeaways You do not need to guess where your energy goes. You can measure it. You can manage it. And you can align it with your production strategy. Ready to Strengthen Your Energy Strategy? If you want to move beyond basic monitoring and build a structured energy optimisation framework, Prescient Technologies can help. Explore how PowerConnect and Prescient’s digital factory expertise support your journey from energy visibility to measurable performance improvement. Contact Prescient Technologies today to strengthen your manufacturing energy strategy.
Read More- March 2 2026
- systemadmin
How Intelligent CAD Validation Reduces Engineering Rework and Design Errors
Have you ever released a design to manufacturing and then discovered errors that forced you back to the drawing board? Rework delays your launch and adds cost. It also affects your team’s confidence. Manufacturing companies in North America, Europe, and India face growing pressure to deliver accurate designs faster. Engineering and R&D teams deal with complex assemblies and tight tolerances. Factory owners expect fewer defects and better coordination between design and production. You may already use advanced CAD tools. But without CAD design validation software, design errors can slip through. Intelligent validation tools help you catch issues early and reduce costly iterations. The Real Cost of Engineering Rework Engineering rework is not just a technical issue. It affects your timelines, budgets, and customer satisfaction. The engineering software industry is evolving rapidly due to automation, AI, and digital integration. Companies now focus on precision and faster product cycles. Yet manual validation processes still cause: When these problems are detected late, you spend extra hours correcting models. You may also need to retool or scrap parts. A recent article on TechCrunch highlighted how AI-driven engineering tools are reshaping product development and reducing manual design errors. Industry leaders now stress the importance of embedding validation early in the design cycle. You may ask, how to reduce rework in product design without slowing innovation. The answer lies in intelligent and automated validation. What is Intelligent CAD Validation? Intelligent CAD validation uses automated CAD checking tools to verify design intent, standards compliance, and manufacturability rules. Instead of relying on manual review, the system automatically checks: This approach shifts error detection from late-stage review to real-time validation. You receive feedback while designing. Industry reports from sources such as Wired and The Verge have discussed how AI is entering engineering workflows. Design automation now supports generative design, simulation, and rule-based validation. Intelligent validation is a natural extension of this shift. How CAD Design Error Prevention Works in Practice 1. Rule-Based Validation Your engineering team defines validation rules based on manufacturing standards and past error patterns. The system checks each model against these rules. If a parameter violates the standard, the tool flags it immediately. This helps you achieve CAD design error prevention before the model reaches production. 2. Real-Time Feedback Modern automated CAD checking tools integrate directly into the design environment. You do not need to export files or run separate scripts. Real-time alerts help you fix errors early. This saves time and protects your project schedule. 3. Design for Manufacturability Checks Design for manufacturability software ensures that your design is production-ready. It verifies: You avoid sending non-manufacturable designs to the shop floor. 4. PLM Integration When you use PLM integrated CAD validation, your validation process connects with lifecycle data. This ensures: Integration bridges the gap between design and production. Why Manufacturing Companies Need Intelligent Validation The global CAD market continues to grow due to automation and the need for precise engineering. As product complexity increases, manual checking becomes less reliable. Manufacturing companies often operate across multiple locations. R&D teams in Europe collaborate with production units in North America or India. Without standardised validation, inconsistencies arise. Intelligent CAD design validation software helps you: You move closer to smart and connected operations supported by smart manufacturing software solutions. Connecting Validation to Smart Manufacturing Smart factories rely on connected systems such as MES, IoT monitoring, and digital twins. Design data feeds directly into manufacturing systems. If your CAD models contain errors, downstream systems inherit those problems. This affects machine settings, production planning, and quality control. Intelligent validation strengthens your digital thread. It ensures that only accurate and compliant models move forward. When combined with platforms like factoryCONNECT and machineCONNECT, validation becomes part of a larger digital ecosystem. Your design data flows smoothly into production monitoring and analytics. Measurable Benefits You Can Expect Reduced Engineering Rework Early detection of errors means fewer design iterations. You save engineering hours and reduce production delays. Faster Time to Market Automated checks remove bottlenecks in design review. Your product development cycle becomes more predictable. Improved Collaboration With PLM integrated CAD validation, teams across locations work on a single source of truth. Lower Manufacturing Costs Design for manufacturability software reduces scrap and retooling. You avoid costly late-stage corrections. Better Compliance Validation ensures adherence to internal standards and industry regulations. This is critical in sectors such as automotive and aerospace. From Problem to Prevention Many organisations are problem aware. They know rework is expensive. But they still rely on manual inspection and experience-based reviews. A shift towards intelligent CAD design error prevention changes your approach. Instead of correcting mistakes, you prevent them. This aligns with broader trends in AI-driven engineering discussed by TechCrunch and Wired. Automation and machine learning are becoming core to industrial software. You do not need to overhaul your entire system at once. Start by introducing automated CAD checking tools that integrate with your existing CAD and PLM environment. Why Choose a Specialist Engineering Software Partner Prescient Technologies has been working in CAD/PLM and engineering software development since 2000 . The company specialises in advanced CAD solutions and digital factory systems. Its expertise in CAD/PLM software development and digital factory integration positions it well to build intelligent validation capabilities . When you combine CAD design validation software with digital factory tools such as factoryCONNECT, machineCONNECT, and powerCONNECT, you create a strong foundation for error-free production. Key Takeaways You can reduce errors before they reach the shop floor. You can improve collaboration across geographies. You can protect your margins in a competitive manufacturing landscape. Ready to Reduce Rework in Your Engineering Process? If you want to understand how to reduce rework in product design and build a structured validation framework, Prescient Technologies can help. Explore how factoryCONNECT and Prescient’s custom CAD/PLM development services can strengthen your validation process and connect design with production. Contact Prescient Technologies today to learn how intelligent CAD validation can support your journey towards smarter manufacturing. when the external environment is challenging.
Read More- February 26 2026
- systemadmin
Why are Global Steelmakers Betting on Digital Twin Technology?
The global market is demanding a version of steelmaking that is faster, cleaner, and significantly more efficient. Why? Decades-old infrastructure in some regions, massive capital assets, and a workforce where traditional knowledge is going out as the older generation of labor enters retirement. The industry-wide pressure for modernization is driven by rising energy prices and unstable raw material costs. Add to that aggressive sustainability targets that look more like mandates than goals. In this environment, digital twin technology is moving into the limelight as a survival kit. The process is about creating a living, virtual replica of a physical asset that mirrors real-time operations, allowing engineers to peek into the future. 1. Defining the Global Steel Digital Twin A digital twin in steel manufacturing is a dynamic computerized simulation of a real, physical object, process, or complete production system. Unlike a static CAD model, a digital twin is continuously linked to plant data available through sensors, distributed control systems (DCS), historians, andmanufacturing execution systems (MES). In a steel plant, these twins are applied to all the high-stake assets; 2. Operational Value Drivers for Digital Twin in Steel Plants 2.1 Predictive Maintenance – Extend Asset Lifecycle Continuous operation means failures occur at any time, and traditional maintenance is either reactive or preventive. Both are inefficient. Digital twins are revolutionizing maintenance with AI-powered pattern recognition. By monitoring vibration, temperature, and acoustics, the system can identify the “digital signature” of a failing part before a catastrophic breakdown. For example, a digital twin can identify unusual vibrations in a rolling mill and allow maintenance to be scheduled proactively. This reduces unplanned stops by up to 30% and extends the lifespan of critical equipment. 2.2 Quality Control – Deliver with Precision, at Scale Ensuring product quality is a big concern as customer specifications from automotive and aerospace sectors become more stringent. Small variations in chemical composition or temperature can lead to costly rejections. If the twin detects a temperature drift, it can recommend immediate adjustments. In some advanced setups, these adjustments are handled autonomously by AI agents. This is where technologies like iNetra (an AI vision inspection system) become essential. By integrating intelligent sensing, steelmakers can conduct end-of-line inspections that catch flaws invisible to the human eye, ensuring every ton meets requirements. 2.3 Energy Efficiency – the “Green Steel” Imperative The global steel industry is under immense pressure to decarbonize. Sustainability is the defining trend for 2026 and beyond. Managing energy consumption is crucial for cost control and ESG compliance. With digital twins, manufacturers can simulate different scenarios to find the most energy-efficient path. For instance, a twin of an electric arc furnace (EAF) can suggest changes in energy input based on the specific material composition of the scrap being melted. When combined with an Energy Management Information System (EMIS) like powerCONNECT, these twins provide the granular data needed for real-time energy monitoring. It helps enterprises reduce power consumption and align with net-zero target roadmaps, without sacrificing production speed. 3. Integrating with Legacy Systems and Data Silos Most steel manufacturing facilities rely on legacy systems. They have layered, incompatible systems added and linked over decades. Here, the primary hurdle isn’t the AI; it’s the data. Data is often trapped in siloed systems across legacy setups. For instance, maintenance logs are stored in one database, sensor data in another, and production metrics in a third. For a digital twin to work, clean data is required, but many plants still depend on manual paperwork rather than a centralized system. Successful digital twin implementations involve a modular approach, as a complete system overhaul can introduce massive operational risks. There are also hardware issues to sort. Standard sensors cannot be near a blast furnace. High-temperature environments impact sensor durability and lead to signal noise. Manufacturers are looking for advanced sensing solutions that include damage-resistant insulation and humidity control. It ensures the data reaching the twin is accurate. 4. Digital Autonomy for a Resilient Future Global digital twin market size is anticipated to exceed US$240 billion by 2032, with manufacturing sector adopting the technology faster than other industries. It is not just a trend anymore. It is a fundamental shift in how steelmakers can grow in a volatile, high-stakes industry. Because steel manufacturing is energy-intensive, physics-heavy, and involves extreme environments, it is an ideal process for digital twin implementation. For steelmakers considering digital twins, a key takeaway is the resilience. With volatile raw material prices and a shrinking workforce, the technology provides a layer of stability. Enterprises can ensure that the expertise of existing operators is codified into the system and that the furnace keeps running at peak efficiency even when the external environment is challenging.
Read More