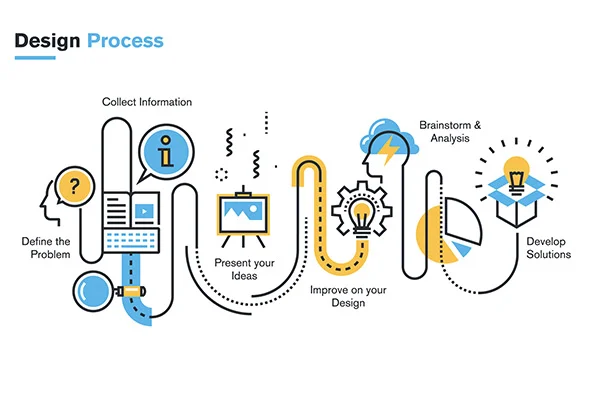
8 Phases of New Product Development
Table of content Ideating or initial ideas Idea screening Concept design & development Business analysis Modeling Test marketing New product launch Difference between New Product Development & Industrial Design You are a seasoned design professional or a talented individual with a great idea and an impeccable design. But you don’t know how to push your idea to life. There are more foundational aspects to a great product, which finally work upon each other to build excellent output. To stay ahead of competitors and to changing market demands, companies need a continuous barrage of new ideas and designs which need to be converted into a tangible products. Success is the prime end game of this business; failure is a no-go zone, especially when odds are at stake against you. Errors and mistakes are unwelcomed in this game; hence there is a proven road for companies to consider when deciding on creating a new product. This blueprint for a new product lays down a systematic, customer-driven new product development process that ensures an orderly progression, as shown below. This section outlines and explores the various early stages of the industrial design process that a product goes through. It does serve as a reasonable account of the overall and general product design process. Ideating or initial ideas Before any design work can begin on a product, there must first be a definition of what the product or product line might be. It involves relentless brainstorming for a skeletal model keeping its usability, aesthetics, and target market in mind. The idea’s genesis can be due to many factors such as: Idea screening An idea can be excellent, good, moderate, or very bad. Once a suitable product opportunity has been identified, a specification document or design brief is created to define the product. It is usually made by a company’s higher management, who’ll have access to information, such as budgeting and buyer/seller feedback. This step involves filtering out the reasonable and feasible ideas which maintain the technical integrity while staying within realistic cost expectations. Features such as a mechanical specification or a reference to an existing invention the product might be based upon are outlined. Expectations uses and underlying intelligence associated with the product are also included. Electronics may also be mentioned, including sounds, lights, sensors, and other specific inputs, such as colors and new materials. Finally, a few reference sketches or photo images can be added to convey a possible direction. Concept design & development All ideas that pass through the screening stage are turned into concepts for testing purposes. A concept is a detailed strategy or blueprint version of the idea. In most companies, designers work up a design brief or product specification that guides their designs. It’s the designer’s role to make these ideas a reality. A professional designer can provide a large variety of designs quickly and efficiently. Many people can draw one or two ideas, but when asked to elaborate, they often fall short. What separates the true design professional is the depth and breadth of their presented ideas and vision clearly and concisely. Concept design generally means using hand-drawn or digital sketches to convey what’s in a designer’s mind onto paper or a screen. Business analysis Once the company has finalized the product outline and marketing strategy, it has to conduct a business evaluation to assess the alluring factor of the proposed new product. It requires a business analysis that involves sales, costs, and profit projections to find the potential success of the new product. Detailed business analysis is needed to determine the feasibility of the product. This stage determines whether the product is commercially profitable or not, whether it will have a regular or seasonal demand and the possibility of it being in the market for the long run. Companies look into sales history, analyze changing market trends, and study target market demands to ascertain a probable demand forecast for the product. Keep in mind that customer perspective and feedback is essential than a company’s perspective of the product. Modeling With the help of 3D modeling software (CAD – Computer Aided Design), the ideas/concept is rendered a shape, thereby creating a 3D model. The technical and engineering team has the biggest workload during this phase. These 3D models will often show problematic areas where the theoretical stresses and strains on the product to be developed will be exposed. If any problem persists, it is the best phase of product development to handle the design errors and devise modifications to address them. Prototyping & pilot runs (preliminary design stage) In this stage, prototypes are built and tested after several iterations, and a pilot run of the manufacturing process is conducted. This stage involves creating rapid prototypes for a concept deemed to have business relevance and value. Prototype means a ‘quick and dirty’ model rather than a refined one that will be tested and marketed later. Adjustments are carried out as required before finalizing the design. Test marketing Apart from continuously testing the product for performance, market testing is also carried out to check the acceptability of the product in the defined market and customer group. It is usually performed by introducing the new product on a very small scale to check if there are any shortcomings. It helps to know in advance whether the customer will accept and buy this product on launching in the market. Test marketing is a powerful tool indeed. New product launch This is the final stage in which the product is introduced to the target market. Production starts at a relatively low volume level as the company develops confidence in its ability to execute production consistently and market abilities to sell the product. Product manufacturing expenses depend on the product’s density if there are numerous parts, material selection, etc. The organization must equip its sales and customer service entities to address and handle queries. Product advertisements, website pages, press releases, and e-mail communications are kept on standby on the launching day. Difference between
Read MoreNew Product Development: Desktop tool vs on Cloud?
Desktop-based product or Cloud-based product? When developing a new product it is always a central question and now with more and more traditional desktop products are moving to the cloud it makes a lot of sense to give this question serious consideration. This article tries to go into details of various aspects that one has to weigh while making this decision. When we trace the origins of the Computer-Aided Design system (CAD) back in the middle of the 20th century, a mainframe was supposed to be the hardware. The software was primarily built by large corporations that could afford to operate mainframes and develop their CAD. With time, the mainframe was supplanted by minicomputers, and CAD became commercially available with a much affordable price tag. Later on, evolution in hardware brought about the microcomputer. Personal Computers and Unix workstations grew in popularity with companies and independent vendors, professionals alike. A remarkable aspect was that CAD systems could ride upon the local processing power of the PC without the need for a centralized server. All data storage was done centrally in the case of mainframes and minicomputers. An operator could log on and access data from any terminal. On the contrary, everything was managed locally in case of microcomputers hence the data was difficult to access unless one had his dedicated PC. To counter this issue, dedicated corporations introduced client/server architectures to facilitate local processing and centralized data storage. Nowadays, companies either manage their hardware and software on their premises, or offload everything to the cloud, or maybe somewhere in between. The new nomenclature was introduced to make distinctions: either “on-premises” (also called as “on-premise” and “on-prem”) or for true cloud-native solutions, it is “Software-as-a-Service” (SaaS). There are many other hybrid solutions, but this article solely focuses on these two aspects. For many design decisions, the most important thing is to know the requirements. In the end, we need to solve a given problem as efficiently as possible. One of the most debated topics in the world of Product development is: Whether to go for a desktop or a web-based solution for New Product Development. Now let’s look at the most common non-functional requirements, which play a role in the design choice between desktop and web: Deployment aka Set-up effort: Deployment refers to how easy and fast one can set-up the required tooling and the runtime for executing a system. Usually this is mainly referring to the developer tooling and its runtime(s) since it needs to be repeated for every developer. Portability: This refers to how difficult is it to port a tool to another platform/hardware. The typical case is accessing all development resources from any platform, e.g. also on your mobile device.Performance and responsiveness: Performance and responsiveness refer to how a tool performs and its responsiveness to users or functionalities. Usability: Usability refers to the level to which a software can be used by specified users to achieve specific project goals with accuracy, effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction. Online Data Storage: Data storage for a Cloud-based app is typically done on cloud-based servers. It makes it very easy for the users to access this data from anywhere using any device. Collaboration: A cloud-based product is more suitable for collaborative development. Cost: Cost is probably one of the most important criteria to consider. The cost takes to form an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), tooling, extension, or the required development runtime. Let us understand these in some detail now. 1.Deployment Deployment is probably the most prominent advantage that is advertised for web-based solutions. The intention is to simply log into a system via a browser and start coding without installing anything specific. Further, you do not need to install any updates anymore, as they are applied centrally. The first interesting aspect of this is how much time you can save with improving the installability. This is connected to the number of developers that you have on-board to use the tooling and the number of people who are occasionally using those tools. Further, it plays a role in how long a developer would use the tool after installation, the shorter the usage the more significant the set-up time would be. One of the important aspects related to installability that needs consideration is updatability. While of course an update to the tooling is hopefully not the same as installing it from scratch, most considerations we had for the installability should be applied for the update case as well. 2 Portability Portability is the second most advantage of a cloud-based solution over a desktop-based. Portability is considered as the ability to access the tool from anywhere on any device. It facilitates access to tooling and runtime through any device with a browser. As a result, you can ideally fulfill your development use case at any location, even from a mobile device. A disadvantage of a pure cloud-based solution is that they often rely on a constant internet connection. While this issue becomes less and less relevant, at least it must be considered. Some cloud-solutions already provide a good work-around, e.g. the offline mode of Google Mail. 3 Performance Performance is a very interesting requirement to consider. In contrast to deployment and portability, there is no clear winner between desktop-based and cloud-based tooling. One can find valid arguments for both to be superb performers. The major reason for this tie is the fact that we have to consider the specific use case when talking about performance. While writing code, engineers need fast navigation, key bindings, and coding features. Although IDEs have caught up a lot in recent years, a desktop tool is typically more performant for those local use cases. However, in cases such as compiling, a powerful cloud-instance can certainly compile a project faster than a typical laptop. 4 Usability Usability also doesn’t have a clear winner in the comparison between desktop-based to cloud-based IDEs. While advocates of both platforms would claim a clear advantage, this is a matter of personal taste. Nowadays, web technologies
Read MoreOutsourcing Product Development
Outsourcing development activities has become an essential component of any successful business strategy these days. As the global competitive market is gradually changing, product based companies are going against established norms following the trend of outsourcing activities. This article discusses about the logic behind outsourcing product development, elaborates on its benefits and discusses the other aspects to be considered when outsourcing product development. What is Outsourced Product Development? The outsourcing of specific activities or all activities related to the development and maintenance of a product is known as Outsourced Product Development. Outsourcing enables product companies to get access into an untapped product-building expertise and global talent pools available with service providers. This helps in exchange of technology and varied work-process. Why Outsource Product Development? Every decision making panel of an organization stumbles upon a vital question—whether to develop a product in-house or outsource the same to a third-party expertise. The product development market is becoming more competitive and mature. As the competition intensifies, product companies are under immense pressure to periodically release new versions in the market. Being an intensive activity, product development requires a lot of attention. The top management can’t afford to put all the emphasis on one activity, while overlooking the other phases of product development. It will end up affecting the profitability of the company. When to outsource product development? A typical product lifecycle involves the following activities: product development, product reengineering and migration, product maintenance, product implementation, and product testing. A product based company can choose to outsource one or more of these activities or it can outsource the entire string related to a particular product to a service providing firm. The question, however remains as to when outsource an activity. There are several factors to be taken into account before outsourcing product development. It varies with company to company. Sometimes it is even seasonal and based on current marketing trends. Some factor can be summarized like this: Benefits of outsourcing product development OPD has many benefits. A product owner need not worry about the outcome or excess expenditure if the activity is in right hands. Correct and well planned outsourcing saves a product company time, expenditure on systems and manpower, legal hassles. The best part is exchange of domain knowledge between the product company and the OPD, something that ensures better output in the future.
Read MoreNPD/ID vocabulary
Bill of materials (BOM): A table containing a list of the components and the quantity of each required to produce an assembly. Brief: Instructions and requests provided to design team prior to the commencement of a project. Business analysis: The practice of identifying business needs and determining solutions to business problems. Commercialization: The process of introducing a new product or production method into the market. Concept design: An early phase of design process, where the broad outlines of function and form are articulated. Ergonomics: Application of principles that consider the effective, safe and comfortable use of design by humans. Ideation: Idea generation or brainstorming. Industrial design: The process of designing products used by millions of consumers around the world. Market research: An organized effort to gather information about target markets or consumers. New product development (NPD): The complete process which involves transformation of a market opportunity or product idea into a product available for sale. New Product Introduction (NPI): New product introduction is the complete process of bringing a new product to market. Patent: An exclusive right granted to an inventor by a sovereign authority, for a specified time period. Pilot Run: An initial small production run produced as a check, prior to commencing full-scale production. Prototyping: An early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process or built to act as a commodity to be replicated or learned from. Sketch: An image that is quick to generate and does not contain complete detail. S.W.O.T: Analysis framework for a company relative to its competitors, market, and industry: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats. Test marketing: An experiment conducted by companies to check the viability in the target market before full scale manufacture.
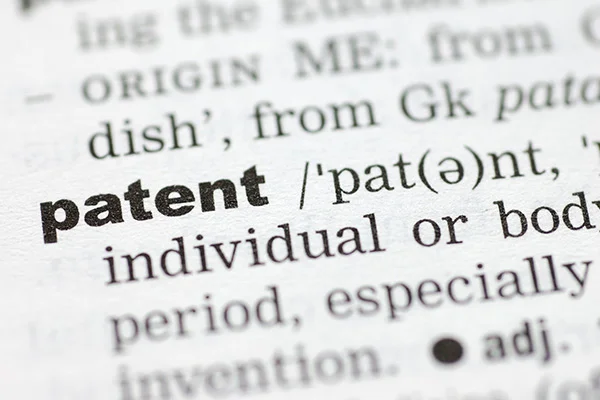
Read MoreWhat is a Patent?
Before you get an answer to that question, take a moment to ask yourself – what are the advantages of having a real estate property to your name? On similar terms, patent is an intellectual property that has all the advantages stated above and one needs to claim it on his/her name. A patent is the granting of property right to an inventor, by a sovereign authority. This grant provides the inventor exclusive rights to the design, or invention for a designated period (usually 20 years), in exchange for a comprehensive disclosure of the invention. Patent process is generally invoked when the product/process I provides a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to an existing problem. Filling for a patent comes with many advantages. Understanding the pros can enable an inventor to make an informed decision. Advantages of Patents
Read MoreThe New Product Development Process
You might be a seasoned design professional thinking “What do my bosses sit around and do all day while I do the real design work”. This section outlines and explores the various early stages of the industrial design process that a product goes through. It does serve as a reasonable account of the overall and general product design process. Ideating or initial ideas Before any design work can begin on a product, there must first be a definition of what the product or product line might be. The idea’s genesis can be many factors such as: Keeping up with the competition Staying ahead of the competition should always be the primary goal for any business. And increased competition is one of the major reasons leading to go for new products development. New products give us a competitive advantage over our rivals. Every firm struggles to fulfill and retain consumers by offering exceptional products. To offer more competitive advantage over the other and to satisfy consumer needs more effectively and efficiently, the product innovation seems to be needed. Consumer demand – Reviews & feedbacks from the customers or even their ideas can help companies generate new product ideas. Internal sources – Companies provide incentives and perks to employees who come up with new product ideas Market research – Companies constantly review the changing needs, requirements and trends of the market by conducting plethora of market research analysis. Competition – Competitors SWOT analysis helps companies to generate ideas. Idea screening An idea can be excellent, good, moderate or very bad. Once a suitable product opportunity has been identified, a specification document or design brief is created to define the product. It is usually created by the higher management of a company who’ll have access to information, such as budgeting and buyer/seller feedback. This step involves filtering out the good and feasible ideas which maintains the technical integrity while staying within realistic cost expectations. Features such as a mechanical specification or a reference to an existing invention the product might be based upon, are outlined. Expectations, uses, and underlying intelligence associated to the product are included as well. Electronics, including sounds, lights, sensors, and any other specific inputs, such as colors and new materials may also be mentioned. Finally, a few reference sketches or photo images can be added to convey a possible direction. Concept design & development All ideas that pass through the screening stage are turned into concepts for testing purpose. A concept is a detailed strategy or blueprint version of the idea. In most companies, designers work up a design brief or product specification that guides their designs. It’s the designer’s role to make these ideas a reality. A professional designer has the ability to provide a large variety of designs in a quick and efficient manner. Many people can draw one or two ideas, but when asked to elaborate they often fall short. What separates the true design professional is depth and breadth of their presented ideas and vision in a clear and concise manner. Concept design generally means the use of hand-drawn or digital sketches to convey what’s in a designer’s mind onto paper or a screen. Business analysis A detailed business analysis is required to determine the feasibility of the product. This stage determines whether the product is commercially profitable or not, whether it will have a regular or seasonal demand and the possibilities of it being in the market for the long run. Modeling With the help of 3D modeling software (CAD – Computer Aided Design), the ideas/concept is rendered a shape, thereby creating a 3D model. The technical and engineering team has the biggest workload during this phase. These 3D models will often show up problematic areas where the theoretical stresses and strains on the product to be developed will be exposed. If any problem persists, it is a best phase of product development to handle the design errors and come up with modifications to address the same. Prototyping & pilot runs (preliminary design stage) In this stage, prototypes are built and tested after several iterations and pilot run of the manufacturing process is conducted. This stage involves creating rapid prototypes for a concept that has been deemed to have business relevance and value. Prototype means a ‘quick and dirty’ model rather than a refined one that will be tested and marketed later on. Adjustments are carried out as required before finalizing the design. Test marketing Apart from continuously testing the product for performance, market testing is also carried out to check the acceptability of the product in the defined market and customer group. It is usually performed by introducing the new product on a very small scale, to check if there are any shortcomings. This helps to know in advance, whether customer will accept and buy this product on launching in the market. Test marketing is a powerful tool indeed. New product launch This is the final stage in which the product is introduced to the target market. Production starts at a relatively low level of volume as the company develops confidence in its abilities to execute production consistently and marketing abilities to sell the product. Product manufacturing expenses depend on the density of the product, if there are numerous parts, material selection etc. The organization must equip its sales and customer service entities to address and handle queries. Product advertisements, website pages, press releases, and e-mail communications are kept on standby on the launching day. Product development is an ever evolving fluid process and cannot be summed up in a few steps. The entire procedure sees insertion of additional stages or even eviction of a crucial part, depending on the nature of the project. Each group of professionals, whether designers, engineers or marketing, sales; has their role to play in this methodology. It is the company’s responsibility to continuously monitor the performance of the new product.
Read MoreImportance of Product Development(NPD) & Industrial Design(ID) for a business
ver the first fiscal quarter of 2018, Apple accelerated investments in research and development operations spending more than $3.4 billion on new hires and initiatives which will keep the company competitive in a fast-paced tech market. Product development is like the gasoline that keeps the wheels rolling. But what drives companies to spend valuable resources such as time, money, human capital, etc. on new product development? And why is it so important? Here are five reasons: Value for customers The primary reason for any new product development is to provide value to its customers. The increasing demands of customers for innovation & new technology calls for the need to develop new or existing products. Otherwise, there is no reason to pour in huge amounts of money in the first place. Keeping up with the competition Staying ahead of the competition should always be the primary goal for any business. And increased competition is one of the major reasons leading to go for new products development. New products give us a competitive advantage over our rivals. Every firm struggles to fulfill and retain consumers by offering exceptional products. To offer more competitive advantage over the other and to satisfy consumer needs more effectively and efficiently, the product innovation seems to be needed. Changing markets Today’s market is more dynamic as compared to the past; it keeps on changing due to the wide variety of customer needs, all thanks to increased literacy rate, globalized market, heavy competition, and availability of a number of substitute. Consumers are constantly evolving which means their tastes and preferences change with them. It is the changing consumer behavior that drives the innovation and development of products. Plus, it also counters seasonal fluctuations. Explore technology Just as consumer trends drive new products, advances in technology drives companies to invest in new products. If your company has not upgraded its technology arsenal for ten years, count yourself to be at the last one in the queue within a few years. Reputation and goodwill Building image and reputation as a dynamic innovation and creative firm boosts a company’s legacy. The new product development is approached. Company desires to convince the market that it works hard to meet customer’s expectations. In fact, company developing new products frequently has more reputation and can easily attract customers. Industrial design is a very crucial part of the entire new product development process. We are aware of the fact that industrial design develops aspects of a product that create emotional connections with the user. It integrates all aspects of form, fit, and function, hence optimizing them to create the best possible user experience. Industrial design’s role in product development process is to establish the design language of a product, as well as the corporate branding and identity. How successfully a company is able to carry out development or modification, incorporating the ergonomics aspect, can often determine the success of a product in the market. Firms that leave industrial design to the end of the engineering lifecycle, or out completely will struggle to find success in consumer-driven markets.
Read MoreWhat is Industrial Product Design?
Table of content What is Industrial Product Design? What does an Industrial Designer do? Every product you have in your home and interact with is the outcome of a design procedure. After long hours of planning, sketching, rendering, and 3D modeling, all those products have come into being. Not to mention the numerous prototypes and testing, it has finally hit the shelves. The ideation and the procedure to develop a particular product is collectively called the Industrial Product Design process or simply ‘Industrial Design’ (ID). Industrial Product Design is the professional practice of conceptualizing and designing products, which are manufactured through mass production techniques, and eventually used by millions of people worldwide every day. An industrial product design process incorporates inputs from diverse domains such as ergonomics, form studies, studio skills, advanced cad, research methods, design management, materials & manufacturing techniques, and social sciences. What does an Industrial Designer do? An industrial designer’s purpose is to emphasize— the appearance of a product, the functioning, how the product is manufactured, and the value & experience it provides for users. Their sole intent is aimed at improving your life through design. Pioneered by industrial engineers and designers, industrial product design has carried manufacturing processes through a significant transformation, without which we would not have the same living standard we have today. Industrial design optimized and streamlined mass production while bringing in artistic functionality and ergonomics, giving back aesthetically pleasing products to the masses. Industrial product designers affect our daily lives more significantly than we imagine. The prime goal of industrial product design is to increase the usability of a product while retaining pleasing aesthetics and improving already existing products. Nowadays, companies have multidisciplinary teams consisting of strategists, planners, user interface (U)I designers, user experience (UX) designers, engineers, graphic designers, branding professionals, etc. – all working for a singular goal, which is to bring you the best product you have never had before. Such a collaboration opens doors to new ideas and perspectives and allows room for the entire evolution of a great product. Industrial product designers collaborate with engineers, material scientists, manufacturers, and branding strategists to bring their creations to life. It takes months and sometimes years of designing, testing, reworking, and developing before the product finally hits the shelves. Industrial product design is an ever-evolving process that keeps changing with technology, market trends, and socioeconomic factors.
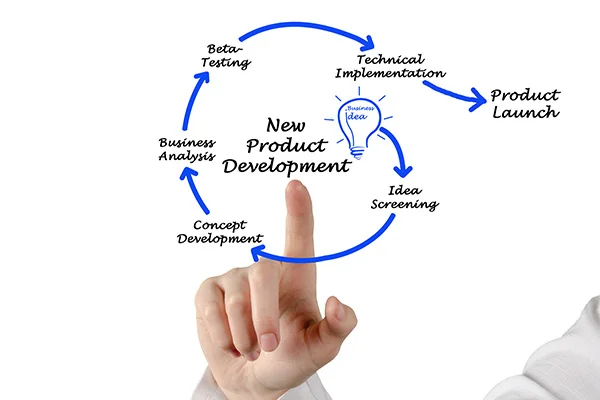
Read MoreWhat is New Product Development?
Often businesses confront consumer preferences, increasing competition and advances in technology; credits to a rapidly changing market scenario. Your business may need to capitalize on an opportunity with the sole intent of getting a monopoly on your respective sector. A common practice of companies is to engage in a process of understanding what their market wants, making smart product improvements, and developing new products that meet and exceed their customer’s expectations. This entire procedure can be termed as ‘New product development’ (NPD). New product development is the process which involves forming strategy, organizing requirements, generating concepts, creating product & marketing plan, evaluating and subsequent commercialization, thereby bringing a new product to the marketplace. ‘New products’ can be: This article explains the importance of NPD and Industrial Design which is a subset of NPD and describes the steps involved.
Read More