Path to Product Development
- Home
- Blog Details
- February 19 2019
- admin
If you are an engineering professional, most likely you are aware of how a physical product comes to life. From the early days of sketching and blueprints, manufacturing of a commodity has come a long way. The modern methodology of creating a product has not only changed drastically, but it has become way more efficient and precise in its approach. Today’s engineer lives and thrives in the world of 3-dimensional models. Whatever masterpiece a designer has in his mind, he has the tools and system to give it life. And it is not just limited to inception of a new idea being turned to a product; it has made the art of reverse engineering being implemented more than ever.
So what are the factors that have revolutionized this craft?
It is the safe to say that with the invention of new tools, techniques and computer, the road to new product development has become more smooth, accurate and flexible. Although a professional can get deep into the subject matter, this article gives a brief overview of the product development from technical perspective.
The footsteps to a new product can be summarized in the following sequence.
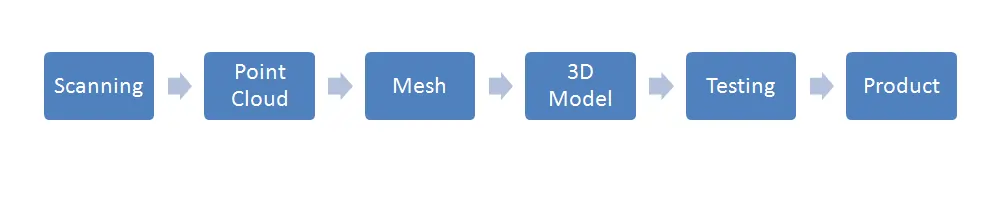
To put it in words, here is how the entire sequence goes:
- Scanning: Whether you have an entirely new idea on your mind, or you want to base your idea on an already existing product; you need a reference. Your reference can be either technical manuals from the manufacturer or the physical product itself. The first step is to scan the product using 3D scanners. 3D scanning technology comes in many shapes and forms. Scanners capture and store the 3D information of the product. The scanned information gets stored in the form of closely spaced data points known as Point Cloud.
- Point Cloud: A point cloud is a collection of data points defined by a given coordinates system. In a 3D coordinates system, for example, a point cloud may define the shape of some real or created physical system.
- Mesh: Point clouds are used to create 3D meshes. A mesh is a network that constitutes of cells and points. Mesh generation involves point clouds to be connected to each other by the virtue of vertices, edges and faces that meet at shared edges. There are specific softwares for carrying of meshing function.
- 3D Model: Once the meshed part is generated, it goes through required software applications to be transferred to Computer Aided Design (CAD) tools to get transformed into a proper 3D CAD model. 3D model is the stage where whole sorts of applications such as sewing, stitching, etc, are implemented to create a prototype.
- Testing: A prototype goes through numerous tests in this phase, to check for limitations and possible calibrations if necessary. This is done to determine the optimum stage where the prototype can be turned to a product.
- Product: This is where the entire process comes to an end. Once a prototype is evaluated and finalized, it is sent for production in order to introduce it to the market.
This introductory part gives you a summary of product development and the related technical terms. In the next chapters, we will dive deep and go through all the mentioned stages, one by one.